How to securely store and validate passwords in your database?
Things NOT to do
-
Storing passwords in plain text is not a good idea because anyone with internal access can see them.
-
Storing password hashes directly is not sufficient because it is prone to precomputation attacks, such as rainbow tables.
-
To mitigate precomputation attacks, we salt the passwords.
What is Hashing?
Hashing is the process of converting input data of any size into a fixed-size string of characters, called a hash value or digest, using a mathematical formula called a hash function. This is a one-way, irreversible process used for efficient data retrieval in data structures like hash tables, and for securing data in applications such as password storage and file integrity verification.
What is salt?
According to OWASP guidelines, “a salt is a unique, randomly generated string that is added to each password as part of the hashing process”.
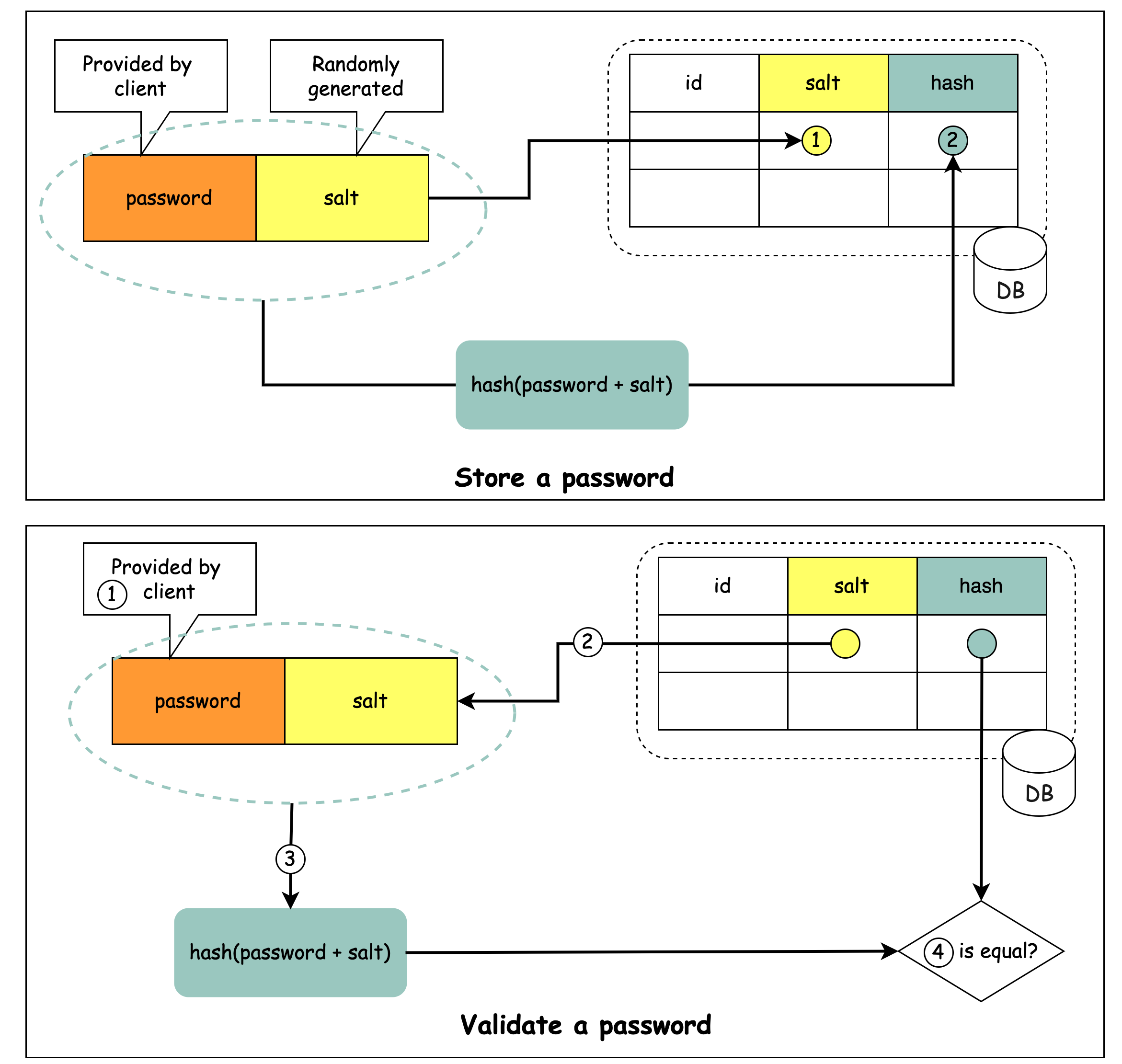
How to store a password and salt?
-
A salt is not meant to be secret and it can be stored in plain text in the database. It is used to ensure the hash result is unique to each password.
-
The password can be stored in the database using the following format: 𝘩𝘢𝘴𝘩( 𝘱𝘢𝘴𝘴𝘸𝘰𝘳𝘥 + 𝘴𝘢𝘭𝘵).
How to validate a password?
To validate a password, it can go through the following process:
-
A client enters the password.
-
The system fetches the corresponding salt from the database.
-
The system appends the salt to the password and hashes it. Let’s call the hashed value H1.
-
The system compares H1 and H2, where H2 is the hash stored in the database. If they are the same, the password is valid.
By A.S.Chauhan on 2025-10-06.